Introduction
What is blockchain consensus?
Blockchain consensus refers to the process by which a decentralized network of computers agrees on the validity of transactions and maintains a consistent and secure ledger. It is a crucial aspect of blockchain technology as it ensures that all participants reach a consensus on the state of the network without the need for a central authority. In simple terms, blockchain consensus mechanisms determine how new transactions are verified and added to the blockchain. There are various consensus mechanisms, with the two most well-known being Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). Each mechanism has its own advantages and disadvantages, and understanding them is essential in comprehending how blockchain networks operate.
Importance of consensus mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in the functioning of blockchain technology. They are responsible for ensuring that all participants in the network agree on the validity of transactions and the order in which they are added to the blockchain. The importance of consensus mechanisms cannot be overstated, as they provide the necessary trust and security for decentralized systems. Without a robust consensus mechanism, the integrity and reliability of a blockchain network would be compromised, making it susceptible to various attacks and fraudulent activities. In the context of blockchain, two popular consensus mechanisms are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). Each mechanism has its own advantages and disadvantages, and understanding their differences is essential for making informed decisions in the blockchain space.
Proof of Work

Definition and concept
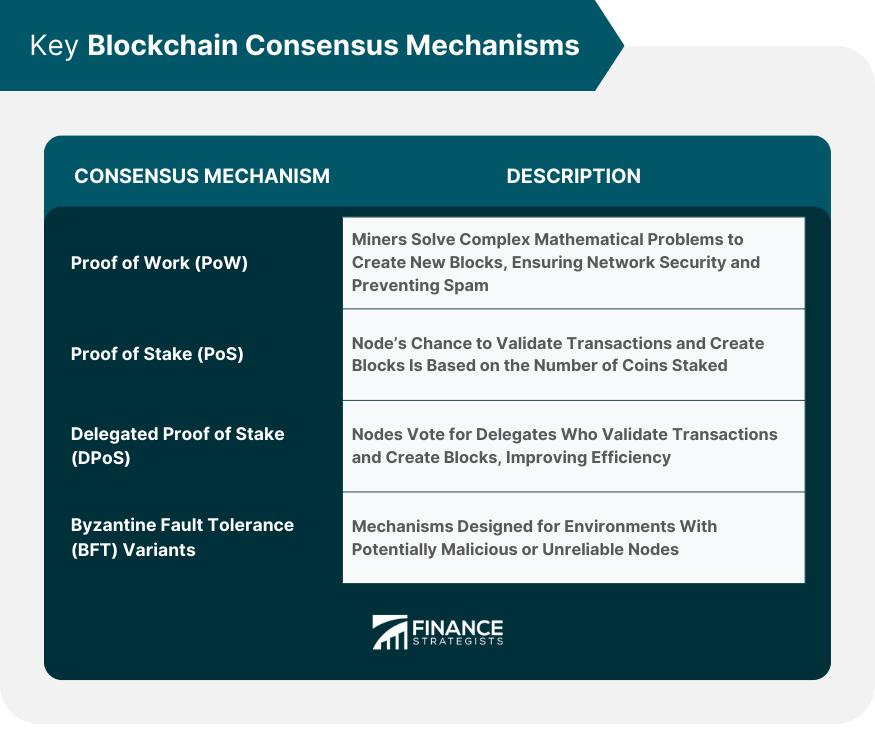
In the context of blockchain technology, consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring the validity and integrity of transactions. The consensus mechanism determines how participants in a network agree on the state of the blockchain and reach a consensus on which transactions are valid. One of the most common consensus mechanisms used in blockchain networks is Proof of Work (PoW). In PoW, participants, known as miners, compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add blocks to the blockchain. Another popular consensus mechanism is Proof of Stake (PoS), where participants hold a certain amount of cryptocurrency as a stake, and the probability of being chosen to validate transactions is proportional to their stake. Both PoW and PoS have their advantages and disadvantages, and understanding these consensus mechanisms is essential for grasping the fundamental concepts of blockchain technology.
How it works
In order to understand how blockchain consensus mechanisms work, it is important to first grasp the concept of decentralization. Blockchain technology operates on a decentralized network, which means that there is no central authority controlling the system. Instead, the network is maintained and secured by a consensus mechanism, which ensures that all participants agree on the validity of transactions and the order in which they are added to the blockchain. Two popular consensus mechanisms used in blockchain are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). Each mechanism has its own unique way of achieving consensus and has its own advantages and disadvantages. Let’s dive deeper into how these mechanisms work and compare them to gain a better understanding of their differences and applications.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages and disadvantages
Blockchain consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. One of the main advantages of PoW is its high level of security, as it requires a significant amount of computational power to solve complex mathematical problems. This makes it difficult for malicious actors to manipulate the blockchain. However, PoW is also energy-intensive and requires a large amount of electricity, which can be a drawback in terms of environmental sustainability. On the other hand, PoS offers a more energy-efficient alternative, as it relies on the ownership of tokens rather than computational power. This reduces the energy consumption associated with mining. However, PoS may be susceptible to centralization, as those with more tokens have more influence over the consensus process. Overall, both PoW and PoS have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them depends on the specific needs and goals of a blockchain network.
Proof of Stake

Definition and concept
Blockchain consensus mechanisms are fundamental to the functioning of a decentralized network. They play a crucial role in ensuring the security, immutability, and trustworthiness of the blockchain. The two most commonly used consensus mechanisms are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). In a PoW system, miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. On the other hand, PoS relies on validators who hold a certain amount of cryptocurrency to validate transactions based on their stake. Both mechanisms have their advantages and disadvantages, and understanding them is essential for comprehending the inner workings of blockchain technology.
How it works
Blockchain consensus mechanisms determine how transactions are validated and added to the blockchain. In the case of Proof of Work (PoW), miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions. This requires a significant amount of computational power and energy consumption. On the other hand, Proof of Stake (PoS) relies on validators who hold a certain amount of cryptocurrency to validate transactions. The more cryptocurrency they hold, the more likely they are to be chosen as validators. This approach is considered to be more energy-efficient compared to PoW. Both mechanisms have their advantages and disadvantages, and their choice depends on the specific goals and requirements of a blockchain network.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages and disadvantages of blockchain consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in understanding their effectiveness and suitability for different use cases. One of the key advantages of the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism is its high level of security. PoW ensures that the majority of participants in the network agree on the validity of transactions, making it difficult for malicious actors to manipulate the system. However, this high level of security comes at a cost, as PoW requires significant computational power and energy consumption. On the other hand, the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism offers a more energy-efficient alternative. PoS relies on the ownership of a certain number of cryptocurrency tokens to validate transactions, reducing the need for extensive computational work. However, PoS is often criticized for being more centralized, as it favors participants with a larger stake in the network. Overall, understanding the advantages and disadvantages of these consensus mechanisms is essential for making informed decisions when implementing blockchain technology.
Comparison of Proof of Work and Proof of Stake

Security
Blockchain consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring the security of a decentralized network. One of the most well-known consensus mechanisms is Proof of Work (PoW), which requires participants, known as miners, to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. This process not only ensures the integrity of the network but also makes it extremely difficult for malicious actors to manipulate the system. On the other hand, Proof of Stake (PoS) is another consensus mechanism where participants are chosen to validate transactions based on the number of coins they hold. This mechanism is considered to be more energy-efficient and cost-effective compared to PoW. However, critics argue that PoS may be more susceptible to attacks if a majority of the participants collude. Overall, the security of a blockchain network heavily relies on the consensus mechanism it adopts, and understanding the differences between PoW and PoS is essential for evaluating the level of security provided.
Energy efficiency
Blockchain consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in the operation and security of decentralized networks. One important aspect to consider when comparing different consensus mechanisms is their energy efficiency. In the case of Proof of Work (PoW), the energy consumption is significant as miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions. This energy-intensive process has raised concerns about the environmental impact of cryptocurrencies. On the other hand, Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism requires validators to hold a certain amount of cryptocurrency as collateral, reducing the need for energy-intensive computations. This makes PoS more energy-efficient compared to PoW. By understanding the energy efficiency of different consensus mechanisms, we can make informed decisions about the sustainability and scalability of blockchain networks.
Decentralization
Decentralization is a fundamental principle of blockchain technology. It refers to the distribution of power and control across a network, rather than being concentrated in a single entity or authority. In the context of blockchain consensus mechanisms, decentralization plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of the network. By distributing the decision-making process among a large number of participants, such as miners or validators, blockchain networks can achieve a higher level of trust and resistance to censorship or manipulation. Decentralization also promotes transparency and reduces the risk of single points of failure, making blockchain systems more resilient and robust.
Other Consensus Mechanisms
Delegated Proof of Stake
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a consensus mechanism used in blockchain networks to achieve consensus and validate transactions. Unlike Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), where all participants can participate in the consensus process, DPoS relies on a smaller number of trusted delegates to validate transactions and create new blocks. These delegates are elected by the network participants based on their reputation and stake in the network. The use of delegates in DPoS allows for faster transaction processing and scalability, as the consensus process is streamlined and efficient. However, it also introduces the risk of centralization, as the power to validate transactions is concentrated in the hands of a few delegates. Despite this limitation, DPoS has gained popularity in many blockchain networks due to its ability to achieve fast and efficient consensus.
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) is a consensus mechanism that plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and reliability of blockchain networks. Unlike Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) which rely on computational power or stake ownership, PBFT focuses on achieving consensus among a group of nodes in a distributed system. This consensus algorithm allows the network to tolerate malicious nodes and maintain the integrity of the blockchain. PBFT is particularly suited for applications that require fast transaction confirmation and high throughput, making it a popular choice in enterprise blockchain solutions.
Directed Acyclic Graphs
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) are an alternative to traditional blockchain structures that offer a different approach to achieving consensus. Unlike a linear blockchain, where each block is linked to the previous one, DAGs use a more complex network of interconnected blocks. In a DAG, each new transaction or block can reference multiple previous transactions, creating a web-like structure. This allows for parallel processing and can potentially increase scalability and transaction speed. However, DAGs also introduce their own challenges, such as the need for a mechanism to prevent double-spending and ensure transaction validity. Despite these complexities, DAG-based consensus mechanisms have gained attention in the cryptocurrency space as a potential solution to the scalability trilemma.
Conclusion

Summary of key points
Blockchain consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of a decentralized network. The two most widely used consensus mechanisms are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). PoW requires participants, known as miners, to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. This process consumes a significant amount of computational power and energy. On the other hand, PoS relies on participants, known as validators, to hold and lock a certain amount of cryptocurrency as a stake. The probability of being chosen to validate a new block is directly proportional to the stake held by the participant. Both mechanisms have their advantages and disadvantages, with PoW being more secure but energy-intensive, and PoS being more energy-efficient but potentially less secure. Understanding the differences between these consensus mechanisms is crucial for anyone interested in the world of blockchain technology.
Future developments in consensus mechanisms
In addition to the existing consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), there are several future developments in consensus mechanisms that are being explored. One such development is the introduction of Proof of Authority (PoA), which relies on a set of trusted authorities to validate transactions and secure the network. Another promising development is the use of Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), where token holders can vote for delegates who will validate transactions on their behalf. Additionally, there is ongoing research on consensus mechanisms like Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET) and Proof of Burn (PoB), which aim to address the energy consumption and scalability challenges associated with PoW and PoS. These future developments in consensus mechanisms show the continuous evolution of blockchain technology and the efforts to improve its efficiency and sustainability.
Final thoughts
In conclusion, when it comes to choosing between Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) as the consensus mechanism for a blockchain, there are several factors to consider. PoW has been the dominant mechanism since the inception of blockchain with the Bitcoin network, and it has proven to be secure and reliable. However, PoW requires a significant amount of computational power and energy consumption, which raises concerns about its environmental impact. On the other hand, PoS offers a more energy-efficient alternative by allowing participants to validate blocks based on the number of coins they hold. This approach reduces the need for excessive computational power and promotes a more sustainable blockchain ecosystem. Additionally, PoS incentivizes participants to hold and stake their coins, which can contribute to the stability and security of the network. Ultimately, the choice between PoW and PoS depends on the specific requirements and goals of the blockchain project, as well as the trade-offs between security, scalability, and energy efficiency.